Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is a central player in the immune system’s early response to infection. Its pentameric structure provides a high-avidity defense mechanism, allowing it to rapidly neutralize pathogens. Yet, despite its critical role, the mechanisms by which IgM exerts downstream functions—particularly through interactions with Fc receptors—remain less explored compared to IgG.
Among these, the Fcμ receptor (FcμR) is an IgM-specific Fc receptor expressed on immune cells including B cells, T cells, and natural killer (NK) subsets. It mediates a range of immunological responses, including B cell survival, early activation, and regulation of antibody-mediated immune communication. To harness the therapeutic potential of IgM, it is crucial to understand how it binds to FcμR at the molecular level.
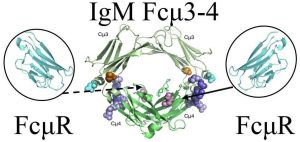
Fig.1 The binding sites of FcμR and Fcμ-Cμ4.1
Structural Overview: IgM and FcμR
IgM is composed of five antibody subunits joined by a J chain, forming a complex 900 kDa pentamer. Each subunit includes constant domains Cμ1 through Cμ4, where the Fc portion comprises Cμ2, Cμ3, and Cμ4. The FcμR, on the other hand, is a type I transmembrane protein featuring a 107-amino acid extracellular immunoglobulin-like domain, followed by a 127-amino acid stalk region, a transmembrane region, and a long cytoplasmic tail.
Key Features of FcμR:
-
Specificity: Binds exclusively to IgM, unlike pIgR or Fcα/μR that can engage both IgM and IgA.
-
Expression Profile: Found predominantly on B cells, T cells, and some NK cells.
-
Functional Role: Contributes to tonic BCR signaling, B cell survival, immune tolerance, and modulates T cell responses.
Dissecting the FcμR Binding Site on IgM
By generating a series of IgM-Fc mutants and evaluating their ability to interact with recombinant FcμR, it is possible to map the critical residues responsible for high-affinity binding. These studies provide not only a structural understanding but also enable the design of engineered antibodies with tunable FcμR engagement.
Key Mutations and Their Effects:
| Mutant | Targeted Residue(s) | Location | Binding Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| WT (Wild-Type) | — | — | High-affinity binding |
| M1 | K361D/D416R | Cμ3 (interface with Cμ4) | Substantially reduced binding |
| M2 | Q510R | Cμ4 | Complete loss of binding |
| M3 | D340S/Q341G/D342S/T343S | Cμ3 (adjacent to Cμ2) | No effect on binding |
Conclusion: Glutamine at position 510 (Q510) in the Cμ4 domain is essential for FcμR binding. Its mutation to arginine (Q510R) abolishes binding entirely, making it a critical target for functional manipulation.
Structural and Biophysical Validation
To ensure that the mutations did not compromise protein integrity, multiple validation steps were performed:
-
Size Exclusion Chromatography with Multi-Angle Laser Light Scattering (SEC-MALLS) confirmed monodispersity and expected molecular mass (~80–84 kDa).
-
Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy showed that all variants retained characteristic β-sheet secondary structures, indicative of proper folding.
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) was used to determine dissociation constants (KD). Wild-type IgM-Fc and the Cμ3-4 fragment both bound FcμR with high affinity (KD ~1 μM), while the M2 mutant showed no detectable binding across all concentrations, emphasizing the critical role of Q510.
Functional Implications of IgM-FcμR Binding
1. Receptor Specificity and Competition
The Cμ4 domain appears to serve as a hub for receptor interactions:
-
FcμR, pIgR, and Fcα/μR all bind this domain, suggesting possible competitive or context-dependent engagement.
-
In polymeric IgM (pentameric/hexameric), residues like Q510 remain exposed, allowing interaction with receptors in circulation.
-
In contrast, Cμ3 interface residues (K361 and D416) may be more relevant in monomeric or membrane-bound IgM, such as the B cell receptor (BCR).
2. B Cell Signaling and Immune Modulation
FcμR cooperates with the BCR in tonic signaling and promotes B cell viability. Using Q510-mutated IgM that cannot bind FcμR provides a valuable tool to dissect:
-
The differential role of soluble IgM vs. membrane-bound IgM
-
Mechanisms of autoimmunity or tolerance mediated via FcμR
-
How pathogens may exploit these interfaces for immune evasion
In fact, the malarial protein PfEMP1 binds to Cμ4, potentially obstructing FcμR engagement—a strategy for immune suppression in Plasmodium falciparum infections.
Scientific Services to Support Your IgM Research
At Creative Biolabs, we offer comprehensive platforms to empower your IgM-focused investigations, from molecular design to therapeutic development.
IgM Production and Purification Service
Our advanced expression systems enable the large-scale production of recombinant or native IgM with high yield, correct polymerization, and optimal biological activity. We offer flexible purification strategies to ensure quality and structural fidelity—ideal for receptor binding studies, therapeutic candidate validation, and functional assays.
Therapeutic IgM Antibody Discovery
Harness the unique potential of IgM in next-generation antibody therapeutics. Our discovery platform includes high-throughput screening, functional characterization, and affinity maturation tailored specifically for IgM, enabling development of candidates with strong complement activation and specialized Fc receptor targeting.
Whether you’re designing FcμR-deficient IgM mutants or developing lead candidates for immunotherapy, Creative Biolabs is your trusted partner in translational IgM research.
Future Directions: Therapeutic and Diagnostic Potential
As our structural understanding of IgM deepens, new opportunities emerge:
-
FcμR-blocking IgM variants could serve as decoys or modulators in diseases where B cell activation is dysregulated.
-
Diagnostic assays can leverage FcμR-specific binding for early B cell profiling or immunodeficiency diagnosis.
-
Next-generation therapeutics can be designed to balance immune activation and suppression by toggling FcμR interactions through engineered Fc domains.
Furthermore, these findings pave the way for rational vaccine design where IgM engagement plays a role in initial immune activation.
Final Thoughts
The elucidation of Q510 in Cμ4 as the keystone of IgM-FcμR interaction marks a turning point in IgM biology. By leveraging this knowledge, scientists can now design antibodies with improved targeting, modulated receptor binding, and greater therapeutic accuracy.
Creative Biolabs is proud to be at the forefront of non-IgG antibody innovation. Our IgM engineering, receptor interaction, and functional assay platforms are ready to accelerate your research. Whether you’re studying autoimmune pathways, infectious disease mechanisms, or exploring antibody-based therapeutics, we offer a comprehensive solution tailored to your goals.
Reference:
1. Nyamboya, Rosemary A., Brian J. Sutton, and Rosaleen A. Calvert. “Mapping of the binding site for FcμR in human IgM-Fc.” Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Proteins and Proteomics 1868.1 (2020): 140266. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.